Everything to know about People Counting with LoRaWAN (Part 1)
In this article, Baptiste Potier and Frederic Tabus give a full run-down on LoRaWAN technology in Smart Buildings, from technical fundamentals to specific applications.
Understanding LoRa and LoRaWAN
LoRa vs. LoRaWAN
“While the two words look the same, LoRa and LoRaWAN have different meanings,” explains Frederic Tabus. “LoRa is a modulation technique for a specific wireless spectrum while LoRaWAN is an open protocol that enables Internet of Things (IoT) devices to use LoRa for communication.” (1,2)
Together, LoRa and LoRaWAN define a low-power, low-cost, wide-area communications protocol that is an excellent fit for sustainable development projects.
“The LoRa network is now global and uses an unlicensed spectrum,” says Frederic Tabus. As LoRa operates in an unlicensed part of the radio spectrum, virtually anyone with a LoRa-enabled device can transmit or receive data freely over the LoRa network. This means global uptake is accelerating.
“As a result, half a billion LoRaWAN devices will be deployed in the world by 2025. We also expect the share of LoRa in US companies’ IoT deployments to grow from 15% to 30% in the next two years.”

LoRaWAN network architecture
There are four essential parts to a LoRaWAN network: end nodes, gateways, a network server, and application servers.
“Starting at the beginning, we have end nodes – also called end devices,” explains Baptiste Potier. End devices are the devices – sensors and actuators – which communicate over the LoRaWAN network.
“These sensors or actuators send LoRa wireless messages to gateways, or receive messages back from gateways. The gateways simply forward messages to the LoRaWAN network server.
“The network server itself is the core of the LoRaWAN architecture. It enables connectivity, management, and monitoring of devices, gateways and end-user applications,” says Baptiste Potier. “The main objectives of the network server are to ensure secure, scalable, and reliable data routing throughout the network,” he explained.
(Image: The Things Industries)
The final part of the LoRaWAN network is the application servers. “Software running on the application servers is responsible for application-specific data processes using data from end devices, producing graphics or displaying data, for example.” Application servers can also generate and send messages to end nodes via the network server.
Using LoRaWAN in Smart Buildings applications
By enabling low-power connectivity of IoT sensors and actuators over a wide area, LoRaWAN brings several opportunities for Smart Building applications. (3)
- Excellent indoor coverage. “The ability for signals to penetrate deep within Smart Buildings is a prerequisite for indoor connectivity, especially in large buildings or those with underground spaces such as parking.”
- Quick installation. “LoRaWAN devices can be easily installed by a non-specialized worker. This makes them particularly suited to the retrofit markets,” explains Baptiste Potier.
- Cheap and simple implementation. Completely private LoRaWAN networks can be set up independently of existing infrastructure, requiring no network operator contracts.
- LoRaWAN takes advantage of an existing worldwide ecosystem.

LoRa Smart Buildings applications
Smart Buildings applications for LoRa can be divided into two categories: technical management applications, directly related to building management systems (BMS), and workspace management applications, which are decoupled from the building management system.
While technical management applications typically deal with heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) and lighting systems, workspace management applications include desk monitoring and building and room occupancy monitoring.
Both of these application types are important in Smart Buildings, explains Baptiste Potier. “All these technologies enable property managers to track building systems, maximize efficiency, and maintain a comfortable and productive work environment, regardless of technical experience.”

Integrating LoRa-driven solutions into Smart Buildings
Smart Building implementations of LoRa-enabled people counting solutions typically use a “Smart Building LoRa gateway” – a LoRa gateway that simplifies connection into the BMS. These can provide straightforward web-based access to manage devices on the network.
“The gateway here acts as a network server and application server,” says Baptiste Potier. “So, the gateway receives and decrypts the data.”
Custom applications can be built on top of the gateway, and signals can be transmitted to the BMS via ModBus TCP or BACnet IP.
LoRa sensors for Smart Buildings
The most common use of LoRa sensors is to help understand the use of different building spaces,” explains Frederic Tabus. “This enables optimization of space and costs while preserving the experience and privacy of building occupants.”
These sensors can be grouped into four families:
- Desk occupancy sensors. Typically placed on each desk, these sensors detect whether a person is seated. Desk occupancy sensors are usually battery-powered.
- Occupancy sensors. Generally battery-powered and ceiling-mounted devices, these can detect the presence of people within an area beneath the sensor – for example, at a desk or workstation.
- Indoor air quality sensors. Also known as comfort sensors, these report air quality metrics such as CO2 concentration to estimate room occupancy.
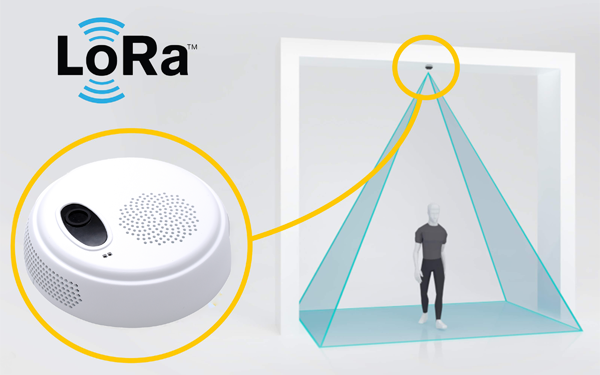
- People counters. People counters are devices that are capable of measuring the flow of people into and out of a space, enabling occupancy metrics for whole buildings and/or parts of buildings to be accurately tracked over time. These sensors are more complex and typically require mains power to deliver accurate data reactively.

Read the second article in this series: “Everything you’d like to know about People Counting with LoRaWAN (Part 2)” here.
References and further reading
- What is LoRaWAN® Specification. LoRa Alliance® https://lora-alliance.org/about-lorawan/
- LoRa PHY | Semtech https://www.semtech.com/lora/what-is-lora
- Why Lorawan® Is The Foundation For Smart Building Success https://lora-alliance.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/LA_WhitePaper_SmartBuildings_0520_v1.1_1.pdf